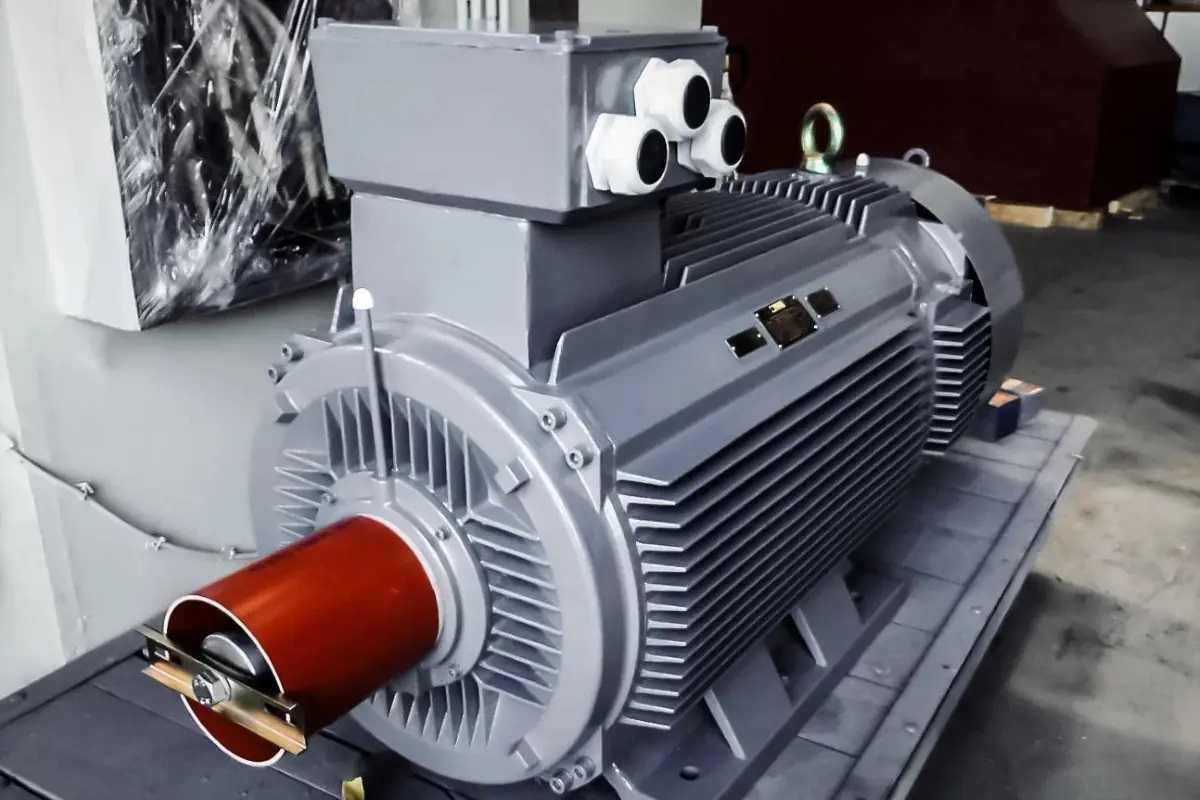
Introduction to Single-Phase Motors
In the world of electrical engineering, motors are the driving force behind countless industrial applications. One type of motor that has gained significant popularity in recent years is the single-phase motor. Unlike its three-phase counterpart, a single phase motor operates using a single alternating current (AC) power source.
Single-phase motors consist of several key components that work together to convert electrical energy into mechanical power. These components include the stator, rotor, and start winding. The stator, which is the stationary part of the motor, contains electromagnets that create a rotating magnetic field. The rotor, on the other hand, is the rotating part of the motor that interacts with the magnetic field to produce motion. The start winding helps initiate rotation by providing extra torque during startup.
Types of Single-Phase Motors
There are several types of single-phase motors, each designed for different applications. Let’s explore some of the most common ones:
1. Capacitor-Start Motor:
This type of motor uses a capacitor to provide an initial boost of power during startup. It offers high starting torque, making it suitable for heavy loads.
2. Permanent-Split-Capacitor Motor:
In this motor, a capacitor is connected in series with an auxiliary winding. It provides a lower starting torque compared to a capacitor-start motor but offers better efficiency.
3. Capacitor-Start Capacitor-Run Motor:
This motor utilizes two capacitors – one for starting and another for continuous operation. It offers both high starting torque and improved efficiency.
4. Shaded Pole Motor:
This simple and cost-effective motor features a series of copper loops around part of the pole. It is commonly used in small appliances and fans due to its low starting torque.
Each type of single-phase motor has its own advantages and ideal applications. By understanding the unique features of each motor, you can choose the one that best suits your specific industrial needs.
How Single-Phase Motors Work
To understand how single-phase motors operate, let’s delve deeper into their working principle. When an AC voltage is applied to the motor, it flows through the stator windings, creating a rotating magnetic field. This field induces a current in the rotor, causing it to rotate. However, single-phase motors face a challenge during startup as they do not possess a self-starting mechanism like three-phase motors.
To overcome this hurdle, single-phase motors rely on start windings and capacitors. The start winding is temporarily connected to the power source during startup, creating an additional magnetic field that helps kickstart the rotor’s rotation. Capacitors, either in series or parallel with the start winding, provide the necessary phase shift required to create the rotating magnetic field.
The Importance of Capacitors in Single-Phase Motors
Capacitors play a crucial role in single-phase motors by aiding their startup and enhancing performance. These electrical devices store and release electrical energy, enabling the motor to generate the necessary torque to overcome inertia during startup. Without capacitors, single-phase motors would struggle to initiate rotation and may experience reduced efficiency.
There are different types of capacitors used in single-phase motors, such as electrolytic capacitors, motor-run capacitors, and motor-start capacitors. Each type serves a specific purpose, whether it’s providing high capacitance for starting torque or maintaining a steady current flow during operation. Choosing the right capacitor is essential to ensure optimal motor performance and longevity.
Practical Tips for Selecting Single-Phase Motors for Industrial Applications
When selecting a single-phase motor for industrial use, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure the motor’s compatibility and suitability for the application. Here are some key considerations:
1. Power and Efficiency:
Determine the motor’s horsepower (HP) rating and look for motors with high power factors and energy efficiency ratings. This will help optimize performance and reduce energy consumption.
2. Voltage and Frequency:
Ensure that the motor’s voltage and frequency match the power supply available in your industrial setup. Single-phase motors typically operate on standard household voltages like 120V or 240V.
3. Motor Enclosure:
Consider the motor enclosure type based on the working environment. Choose an enclosure that provides adequate protection against elements such as dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
4. Frame Size:
Select a motor with a frame size that fits the mounting requirements of your machinery. Common frame sizes for single-phase motors include NEMA standards like 48, 56, and 143T.
5. Thermal Protection:
Look for motors equipped with built-in thermal protection devices such as overload protection or automatic reset features. These protections help prevent overheating and extend the motor’s lifespan.
6. Reversibility:
Depending on your application, you may need a motor that can operate in both forward and reverse directions. Verify if the motor offers reversible functionality to meet your specific needs.
7. Noise and Vibration:
Industrial environments demand smooth and quiet operation. Look for motors that are designed to minimize noise and vibration levels, ensuring a comfortable and efficient working environment.
8. Reliability:
Consider the reputation and reliability of the motor manufacturer. Look for motors from trusted brands with a track record of producing high-quality and durable products.
Seeking guidance from experts or consulting with electrical engineers can greatly assist in selecting the right single-phase motor for your industrial application. Their expertise will ensure that you choose a motor that meets your specific requirements and operates efficiently within your facility.
Real-World Examples of Single-Phase Motor Applications in Manufacturing
Single-phase motors find extensive use in various industries due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. Here are some examples of industrial manufacturing processes where single-phase motors play a vital role:
Conveyor Systems:
Single-phase motors power conveyor belts in industries such as logistics, food processing, and packaging. They provide smooth and reliable movement of goods along the production line.
Pumps:
Single-phase motors drive water pumps used in irrigation systems, swimming pools, and residential water supply. They ensure efficient water circulation and delivery.
Compressors:
Single-phase motors power air compressors, which are essential in applications such as pneumatic tools, HVAC systems, and automotive repair.
Mixers:
Single-phase motors drive mixers used in cooking appliances, bakery equipment, and chemical processing. They enable efficient blending and mixing of ingredients.
Fans:
Single-phase motors are commonly used in ventilation fans, exhaust fans, and air conditioning units. They provide the necessary airflow for cooling and maintaining air quality.
These are just a few examples, but the applications of single-phase motors extend far beyond these. From industrial machinery to household appliances, single-phase motors are prevalent in numerous sectors, contributing to efficient manufacturing processes worldwide.
Harnessing the Potential of Single-Phase Motors
In conclusion, single-phase motors are a vital component of modern industrial manufacturing. Their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make them a popular choice in a wide range of applications. By understanding the different types of single-phase motors, their working principles, and practical considerations for selection, beginners in electrical engineering can make informed decisions when choosing and utilizing these motors.
Remember to consult experts or engineers from Hitachi in Asia for guidance specific to your unique requirements. Their expertise will help ensure that you select the right single-phase motor for your industrial needs, optimizing performance, efficiency, and reliability.
Harness the power of single-phase motors and revolutionize your industrial manufacturing processes with these efficient and reliable electrical devices.